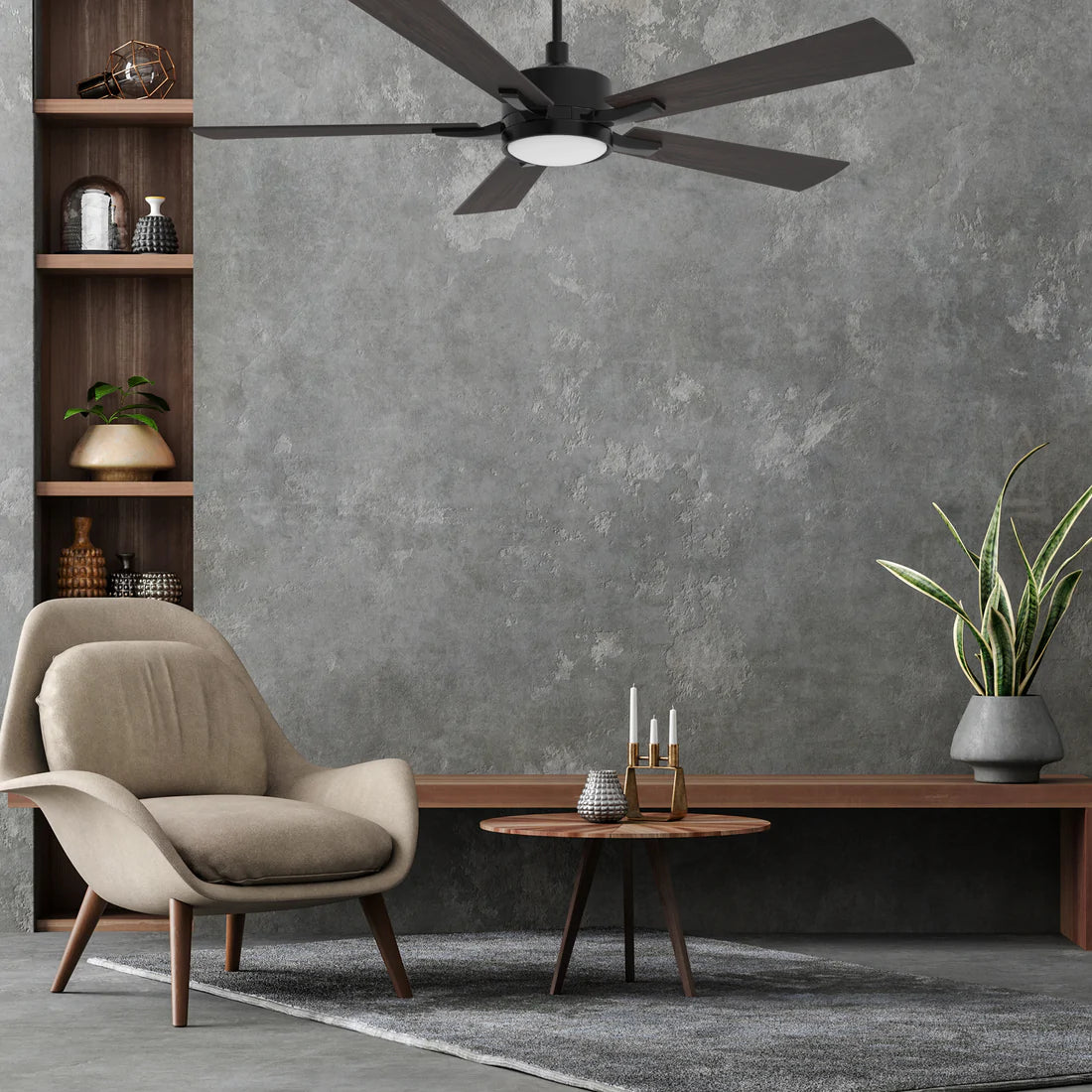
Ceiling fan has been a staple in living space for decades, yet, there is much more you need to know to meet your comfort. In today's blog, we are unveiling the secret of the ceiling fan airflow. We'll break down the meaning of CFM and air velocity and provide additional factors that can contribute to your cooling breeze or can be the cause of your ceiling fan not making you feel cool!
What Is a Good Airflow For a Ceiling Fan
First of all, we need to build up a concept of what is a good airflow for your ceiling fan. A ceiling fan has good airflow means it has a high CFM and Velocity. The ceiling fan has more ability to effectively circulate air and provide comfort in a given space. A "good airflow" means that the ceiling fan can move an adequate volume of air to create the desired cooling or air circulation effect in the room. For personal, we will have a much stronger feeling about wind while under a ceiling fan has a better airflow.
Understanding CFM & Air Velocity
To understand how your ceiling fan functions well, there are two concepts that you definitely need to know. One is the CFM, which stands for Cubic Feet Per Minute, and the other is the Air Velocity. So what is the difference between them?
What Is CFM
So what does CFM mean? CFM is the common measure to quantify the volume of the air movement. It is determined by the cubic feet of air volume moved by the fan per minute. Typically, the higher of CFM amount, stands for the more air the fan moves, resulting in a more noticeable breeze. Normally, the bigger size of the fan will have more power to move more volume of air while running.
How to Calculate CFM
To calculate CFM, it is very simple CFM = Area (in square feet) X Velocity (in feet per minute). But don't worry, you don't need to perform these calculations manually. At Smafan, we provide all of our ceiling fan's CFM data from our own testing lab. You can easily find it in the specification tabs.
About Air Velocity
Air Velocity is also an important value to measure a ceiling fan's airflow. Air velocity refers to the speed at which your ceiling fan moves the air throughout the space. Or more specifically, the higher the air velocity, the less time it will take for you to feel the temperature changing.
In a short conclusion, CFM shows how much the air moved and Air Velocity shows how fast the air moved in a specific room space, which combined to describe the airflow for the ceiling fan. These two factors will affect the ceiling fan's airflow at the same time. For example, if a fan with a high CFM but a low velocity(Like the ones at the gym, large but span slowly), you may not be able to feel it, or at least you won't feel the wind across your skin.
Other Factors that Affect Ceiling Fan Airflow
Although the major factors that impact on the ceiling fan's airflow are CFM and velocity, some factors will change the performance of the CFM and the velocity, since our living space is not like the testing lab. So let's see what factors will have an indirect effect on the ceiling fan airflow.
Ceiling Fan and Room Size
To kick it in, let's begin with the most basic thing you will need to consider before you purchase the ceiling fan, the Size. Not only the fan size itself but also the room size. As we mentioned CFM is to measure how much volume of air fan can move. If your room is quite large but your ceiling fan is small instead, you will hardly feel the high airflow. So the key is to select the best size of ceiling fan for your room. Here is our recommendation for you to choose a ceiling fan based on your room size. You can also check our ceiling fan buy guide.

Ceiling Height
After you decide on your fan size, you should also consider the downrod, or choose the flush mounted version if your ceiling is low. A ceiling fan is designed to create air movement in a specific room. Normally, this room refers to the space between the floor and the ceiling fan itself. When a fan is mounted too close to the floor, such as in a room with low ceilings, it can't effectively circulate air throughout the entire space. Instead, it may create a strong breeze near the floor but fail to reach higher areas.

Also, proper fan placement takes into consideration safety and aesthetics. A fan that is too low can pose safety risks, especially in rooms with high traffic or tall individuals.
Fan Blade Design and Pitch

The fan blade is also the factor that will affect the airflow, however, the number of fan blades is not the essential part. Here are the fan blade factors that you should not miss out on for a good ceiling fan's airflow:
- Blade Material: The material of your fan blades can improve your ceiling fan airflow, or it can cause more air drag. If your ceiling fan blades are made of heavy and dense material, they will limit how fast the motor can rotate the blades. If your fan blades are made of a material that is too light and fragile, they will not have the power to move air throughout the room.
- Blade Angle: While it may not be obvious, your ceiling fan blades are angled. This angle is what pushes air up or down, depending on the ceiling fan's direction. Typically, the higher the fan blade angle, the more air they can move but the more power they require. To create the perfect balance of powerful airflow and energy efficiency, your fan blades should have an average angle between 12 - 16 degrees.
- Blade Shape: Another way to improve the aerodynamics of ceiling fan blades is with innovative blade shapes. Our Smafan Icebreaker Smart ceiling fan is a great example; designed with undulated fan blades, the Icebreaker is one of our collections with the highest CFM ceiling fan, maxing out at 7,000 CFM.
Ceiling Fan Direction
Most ceiling fan models feature reversible motors that allow you to switch the direction of your fan blades. This direction determines whether your ceiling fan is pushing air downwards or lifting it toward the ceiling. During the summer, you want your fan blades to rotate counterclockwise and propel air downwards for a cooling breeze. In the winter, your fan blades should spin clockwise, lifting cool air and blending it with the warm air near the ceiling.

This is also the common issue that we think our ceiling fan has low airflow. Since we might turn on the wrong mode and the ceiling fan direction is wrong. But don't worry, check out our blog content for you to know better about ceiling fan direction.
Ceiling Fan Motor
Without the proper motor, your ceiling fan will not have the power to deliver high CFMs and high air velocities. At Smafan, we provide our customers with different options, the traditional AC motor and the modern DC motor. But what is the difference between these two types of motors?
- AC motors deliver comfortable airspeeds with 3-speed control and an average CFM of 3000 - 5000 CFM.
- DC motors are well known for their increased power and efficiency; they offer 10-speed control and impressive CFMs of up to 7,000.
Smafan Combines the Best of Both
The easiest way to distinguish these two measurements is to consider your ceiling fan speed settings. When you need a strong and cooling wind, you don't adjust your CFM, you set your fan to high speed (high velocity). In this way, the best ceiling fans are the ones with high CFMs and high velocities. Fortunately, Smafan knows the difference and ensures our ceiling fan models can meet the high CFM and hit velocity.
At Smafan, we know that every fan component plays an important role in the final look and feel of your ceiling fan. From the ceiling fan motor to the fan blade materials, Smafan conducts an extensive research and selection process to offer our customers the best performance and design. So check out our DC motor high CFM ceiling fan to select a good airflow ceiling fan for your living space.