Ceiling fans with lights are a popular choice for many homeowners and businesses alike, providing comfort and energy efficiency. However, not all ceiling fans are created equal when it comes to moving air effectively. In this article, we will delve into the factors that determine the airflow of a ceiling fan and discuss how to measure it. We will also explore different types of ceiling fans, from small to large, and provide expert recommendations for the best ceiling fans on the market. So, if you're wondering which ceiling fan moves the most air, read on to find out.
Understanding Airflow and CFM in Ceiling Fans
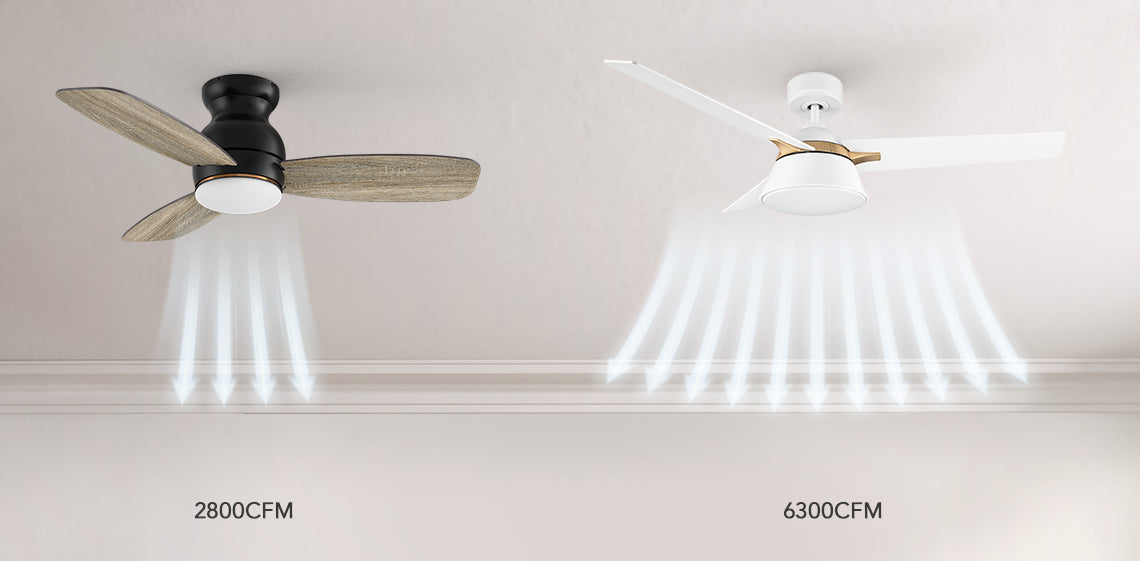
To understand which ceiling fan moves the most air, it's essential to grasp the concept of airflow and CFM (Cubic Feet per Minute). Airflow refers to the volume of air that a fan can move, while CFM measures the efficiency of a fan in terms of the amount of air it can circulate. The higher the CFM, the more air the fan can move.


Ceiling Fan Airflow Factors
To evaluate a ceiling fan's airflow effectively, consider essential elements: ceiling fan blade pitch and size, motor power, RPM, and installation. These factors combine to determine the fan's ability to circulate air efficiently
Fan Blade Pitch: Maximizing Air Movement
Blade pitch refers to the angle of the blades in relation to the fan motor. A steeper pitch means the blades can push more air, leading to better airflow. For example, a fan with a blade pitch of 15 degrees will generally move more air than one with a 10-degree pitch. Imagine a paddle boat - a steeper paddle angle moves more water, propelling the boat faster. Similarly, a steeper blade pitch in ceiling fans pushes more air, increasing circulation.


Blade Size and Quantity: Balancing Efficiency and Space
The size and number of fan blades play a crucial role in determining airflow. Longer blades can sweep a larger area, thus moving more air. However, having too many blades can sometimes reduce efficiency due to increased drag. A typical example is a standard home ceiling fan, which usually has 3-5 blades of moderate length, balancing airflow and efficiency.

Power Motor & RPM: The Engine for Airflow
The motor's power and the RPM (revolutions per minute) are like the engine of a ceiling fan. A more powerful high-quality motor can spin the blades faster, resulting in higher RPM and greater airflow. For instance, a ceiling fan in a gymnasium might have a high-power motor to generate enough airflow to cool a large area quickly.
Blade Material and Design: Crafting for Performance
The material and design of the blades affect their ability to move air. Lightweight materials like aluminum or plastic can be moved faster by the motor, increasing airflow. The aerodynamic design of blades also plays a part, much like the wings of an airplane, where the shape determines the lift and airflow.

Installation Height and Position: Optimizing Air Circulation
The height at which a ceiling fan is installed, and its position in a room, can impact its effectiveness. Fans installed too high might not circulate air efficiently in the living space. For example, in a two-story living room, a fan hanging closer to the ground floor will circulate air more effectively across the seating area compared to one closer to the ceiling.


How to Measure the Airflow of a Ceiling Fan
Measuring the airflow of a ceiling fan is a straightforward process. First, ensure that your fan is on the highest speed setting. Then, position yourself directly beneath the fan and hold a handheld anemometer (a device used to measure wind speed) at chest height. Record the wind speed reading displayed on the anemometer. Repeat this process at different positions in the room to get an average airflow measurement.
Alternatively, you can refer to the CFM rating provided by the manufacturer. Most reputable ceiling fan manufacturers will specify the CFM rating of their products, allowing you to compare different models easily. Keep in mind that the CFM rating should be adjusted for the height of the ceiling. For higher ceilings, a fan with a higher CFM rating is necessary to ensure adequate airflow.

Evaluating Small Ceiling Fans for Compact Spaces
If you have a small room, typically defined as a space less than 150 square feet, or a room with a ceiling height lower than 8 feet, opting for a small or low profile ceiling fan is a wise decision. For such spaces, a ceiling fan with a blade span ranging from 36 to 42 inches is ideal. These small fans are designed to efficiently fit into compact areas without sacrificing airflow and cooling performance. Selecting a low-profile fan for rooms with lower ceilings ensures adequate headroom and effective air circulation, making them perfectly suited for maintaining comfort in smaller, constrained spaces.

When evaluating small ceiling fans, consider their CFM rating, blade pitch, and length. Opt for a fan with a higher CFM rating to ensure sufficient airflow in a compact space. Additionally, a steeper blade pitch and longer blades will help maximize the fan's effectiveness.
One small ceiling fan that stands out for its exceptional airflow is the Bretton Model & Kaze Model & Azure Model. With a CFM rating up to 5270 and a blade pitch of 12 to 18 degrees, this ceiling fan with light moves air efficiently, even in small rooms. Its compact design and low-profile installation make it an excellent choice for spaces with low ceilings.
Medium Ceiling Fans for Optimal Performance in Moderate Spaces
For medium-sized rooms, typically ranging from 150 to 250 square feet, selecting a ceiling fan that balances performance with aesthetics is key. Fans with CFM ratings of at least 5,000, a blade pitch of 11 to 15 degrees, and a powerful motor are recommended. In these spaces, a medium ceiling fan with a blade span of 44 to 52 inches often provides the ideal balance of efficiency and style. The Cresta & Striver Model, with a CFM rating of 5350 and a three-blade design, stands out as an excellent choice for living rooms, bedrooms, and similar sized areas.
Large Ceiling Fans for Expansive Areas
In large rooms, which typically exceed 250 square feet, ceiling fans need to move significant volumes of air to be effective. For such spaces, large ceiling fans with CFM ratings of 7,000 or more and a blade pitch of 12.5 to 16 degrees are ideal. A larger blade span, typically around 60 inches or more, is recommended to ensure extensive air movement. The Icebreaker smart ceiling fans with LED light, with its impressive CFM rating of 7,000 and a 3-blade design, are perfect for large living rooms, spacious dining areas, and other large spaces, ensuring efficient air circulation throughout the area.
Tips for Optimizing Ceiling Fan Airflow
To maximize your ceiling fan's airflow, consider these tips:
- Regular Maintenance: Keep the blades clean and the motor well-maintained. Details refer to How to Clean your Ceiling Fan
- Appropriate Sizing: Choose a ceiling fan size that matches your room dimensions. Details refer to How to choose a ceiling fan size and style.
- Correct Installation Height: Install a ceiling fan at the right height for optimal performance. Details refer to What size of downrod should I purchase.
- Complementary Use with HVAC Systems: Use fans alongside your heating and cooling systems for better air distribution. For details, see Ceiling Fan Direction.
- High CFM Options: For rooms that require stronger air circulation, explore our High CFM Ceiling Fans for models designed to deliver powerful airflow and keep large areas comfortable.
Unlock the Secret to a Cooler, Stylish Home
In conclusion, the efficiency of a ceiling fan in moving air is determined by factors such as blade design, motor quality, CFM rating,blade material, and installation. By considering these aspects, you can choose a ceiling fan that offers both aesthetic appeal and functional efficiency, enhancing the comfort and airflow in your space.
Take the first step towards transforming your space with optimal airflow and design. Explore our exclusive selection of high-efficiency ceiling fans and take advantage of our limited-time offers. Enhance your home’s comfort and style now—your perfect ceiling fan awaits!